Table Of Content
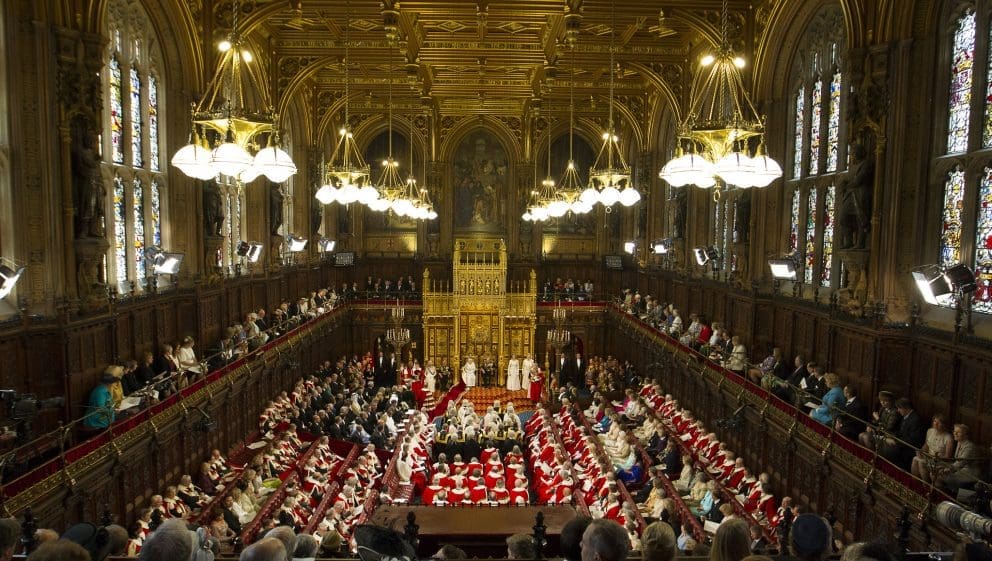

But it did so, repeatedly, at the request of the elected government of the day. That request was made in order to meet the pledge Rishi Sunak made to “stop the boats”, despite polling showing that support for the Rwanda bill was low. In its latest parliamentary round on Monday night, the Lords won a concession from the government over its demands to ensure asylum seekers who had worked with British armed forces abroad were not deported to Rwanda. But after further rounds of so-called "ping pong" saw the bill flit between both Houses throughout Monday evening, both MPs and peers have now agreed to the plan, and it will soon become law - with Rishi Sunak pledging the first flights will take off "in 10 to 12 weeks".
Lords reform
In 1999, the Labour government brought forward the House of Lords Act removing the right of several hundred hereditary peers to sit in the House. The Act provided, as a measure intended to be temporary, that 92 people would continue to sit in the Lords by virtue of hereditary peerages, and this is still in effect. The Conservative–Liberal Democrat coalition agreed, after the 2010 general election, to outline clearly a provision for a wholly or mainly elected second chamber, elected by proportional representation. As an interim measure, appointment of new peers would reflect the shares of the vote secured by the political parties in the last general election.
The tortuous journey of the UK government’s Rwanda plan
The first English Parliament is often considered to be either Simon de Montfort's Parliament (held in 1265) or the "Model Parliament" (held in 1295), which included archbishops, bishops, abbots, earls, barons, and representatives of the shires and boroughs. It also doubles the number of families that plot can support — meaning you’ll get two families for a regular plot or four for a plot with a living space expansion built. With a burage plot (Level 2), you’ll unlock some new backyard workshops for things like a blacksmith, brewery, or cobbler. The important thing to note here is that building these extensions converts the family (or families) on that burgage plot into artisans. That means the only thing families living on that Burgage Plot will do is that activity. And that means, for example, even if you pause the work at a Tailor’s Shop, the family won’t become unassigned and available for other jobs.
Parliament in Recent History
Other public bills cannot be delayed by the House of Lords for more than two parliamentary sessions, or one calendar year. These provisions, however, only apply to public bills that originate in the House of Commons, and cannot have the effect of extending a parliamentary term beyond five years. A further restriction is a constitutional convention known as the Salisbury Convention, which means that the House of Lords does not oppose legislation promised in the Government's election manifesto. Detailed proposals for Lords reform, including a draft House of Lords Reform Bill, were published on 17 May 2011.
House of Lords: What is it and what could Labour replace it with?
Lords of Appeal in Ordinary were first appointed under the Appellate Jurisdiction Act 1876. They were selected by the Prime Minister of the day, but were formally appointed by the Sovereign. A Lord of Appeal in Ordinary had to retire at the age of 70, or, if his term was extended by the government, at the age of 75; after reaching such an age, the Law Lord could not hear any further cases in the House of Lords. The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 resulted in the creation of a separate Supreme Court of the United Kingdom, to which the judicial function of the House of Lords, and some of the judicial functions of the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, were transferred.
Membership
In 1968 the Labour Government of Harold Wilson attempted to reform the House of Lords by introducing a system under which hereditary peers would be allowed to remain in the House and take part in debate, but would be unable to vote. This plan, however, was defeated in the House of Commons by a coalition of traditionalist Conservatives (such as Enoch Powell), and Labour members who continued to advocate the outright abolition of the Upper House (such as Michael Foot). The Lords contains many excellent individuals whose wisdom is much valued by the public sector. But its total of 800 members include many who have been accused of buying seats from political parties with cash or other favours, an accusation that the House of Lords persistently denies. A further quarter of peers are ex-MPs for whom the Lords is an old people’s club and source of modest pension.
There are many options for reform but history demonstrates how tricky reform is. It is widely argued that one of the most urgent reforms needed is to contain the ballooning size of the Lords by restricting the Prime Minister’s power to appoint new peers. As it does not hold a majority, the government is defeated in the House of Lords quite often, generally on amendments to bills.

A cross-party campaign initiative called "Elect the Lords" was set up to make the case for a predominantly elected Upper Chamber in the run up to the 2005 general election. There were no women sitting in the House of Lords until 1958, when a small number came into the chamber as a result of the Life Peerages Act 1958. One of these was Irene Curzon, 2nd Baroness Ravensdale, who had inherited her father's peerage in 1925 and was made a life peer to enable her to sit. After a campaign stretching back in some cases to the 1920s, another twelve women who held hereditary peerages in their own right were admitted with the passage of the Peerage Act 1963. Other things being equal, most parliaments are better with second chambers than without them. But its undemocratic composition deprives it of the legitimacy to impede rather than merely advise the government of the day.
Peers on leave of absence
House of Lords 'bordering on racist' over Rwanda Bill, says deputy foreign secretary - The Telegraph
House of Lords 'bordering on racist' over Rwanda Bill, says deputy foreign secretary.
Posted: Mon, 22 Apr 2024 09:01:00 GMT [source]
The House of Lords cannot delay a money bill (a bill that, in the view of the Speaker of the House of Commons, solely concerns national taxation or public funds) for more than one month. The House of Lords was reduced to a largely powerless body, with Cromwell and his supporters in the Commons dominating the Government. It returned to its former position as the more powerful chamber of Parliament—a position it would occupy until the 19th century. Additionally, there are a half-dozen notable Valyrian weapons whose whereabouts are unknown. Brynden was sent to Castle Black back in 233 AC, and he eventually rose to Lord Commander.
Over course of the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, Parliament and its powers evolved—just as the United Kingdom itself did. The so-called “Stuart Kings”—Charles II and his brother James II, who succeeded him in 1685—maintained a similar relationship with the legislature as their father had in the 1640s. However, religion was a major issue dividing English government and society. Four years later, though, Cromwell disbanded the Rump Parliament and created the Nominated Assembly, a de facto legislature. The son was deposed a year later, and Britain’s government effectively collapsed. From 1603 to 1660, the country was mired in a drawn-out civil war and, for a time, military leader Oliver Cromwell assumed power under the title Lord Protector.
For example, during much of the reign of Edward II (1307–1327), the nobility was supreme, the Crown weak, and the shire and borough representatives entirely powerless.
No comments:
Post a Comment